Colloidal quantum dots are of great interest in application of optoelectronic devices, due to their cost-effectiveness and solution-based processability. Also, size-tunability provides a great advantage for optoelectronic device applications in that the optical properties can be easily engineered. Primarily, lead(II)-sulfide colloidal quantum dots are promising materials for photovoltaic devices due to their strong quantum confinement and high dielectric constant.
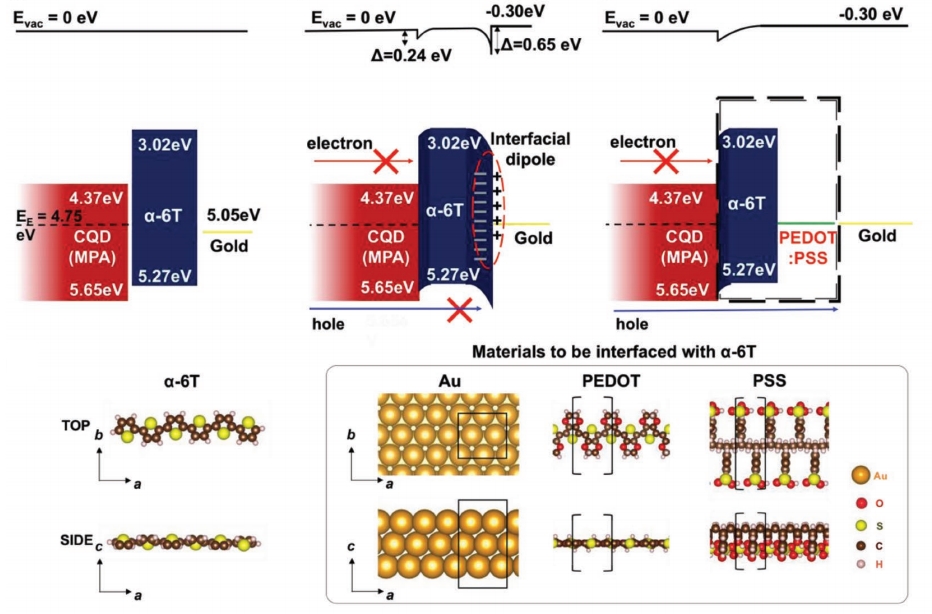
Interface dipole engineering for QD photovoltaics 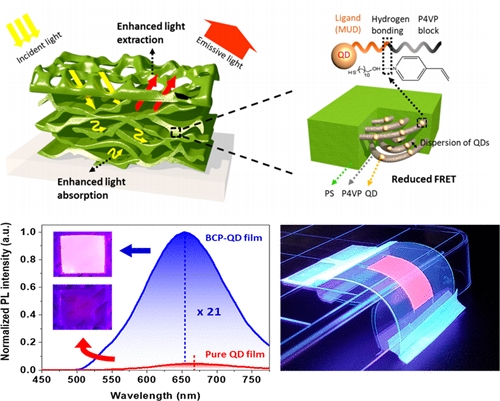
BCP-QD composites for enhanced light emission 
Spray coating of QDs
Further reading
“Suppressing Interfacial Dipoles to Minimize Open-Circuit Voltage Loss in Quantum Dot Photovoltaics” Advanced Energy Materials, 2019, 1901938 Hunhee Lim, Donghun Kim, Min-Jae Choi, Edward H. Sargent, Yeon Sik Jung,* and Jin Young Kim* [Link]
“Order-of-Magnitude, Broadband-Enhanced Light Emission from Quantum Dots Assembled in Multiscale Phase-Separated Block Copolymers” Nano Letters, 2019, 19, 10, 6827-6838 Geon Yeong Kim, Shinho Kim, Jinyoung Choi, Moohyun Kim, Hunhee Lim, Tae Won Nam, Wonseok Choi, Eugene N. Cho, Hyeuk Jin Han, Chul Hee Lee, Jong Chan, Kim, Hu Young Jeong, Sung-Yool Choi, Min Seok Jang*, Duk Young Jeon*, and Yeon Sik Jung* [Link]
“Tuning
Solute-Redistribution Dynamics for Scalable Fabrication of
Colloidal Quantum-Dot Optoelectronics” Advanced
Materials, 2019, 1805886 Min-Jae Choi, YongJoo
Kim, Hunhee Lim, Erkki Alarousu, Aniruddha Adhikari, Basamat S. Shaheen, Yong
Ho Kim, Omar F. Mohammed, Edward. H. Sargent, Jin Young Kim,* and Yeon Sik
Jung* [Link]
